Camm Memory vs Traditional Memory: Which Is Better? in the swiftly advancing realm of technology, innovations often outpace our ability to keep up. One of the most intriguing developments shaking up the hardware landscape is the emergence of Camm Memory. As the industry increasingly looks for faster, more efficient solutions, the debate between Camm Memory vs traditional memory is more relevant than ever.
Whether you’re a tech aficionado or a casual user, understanding the distinctions between these two types of memory could redefine how you perceive device performance and efficiency.
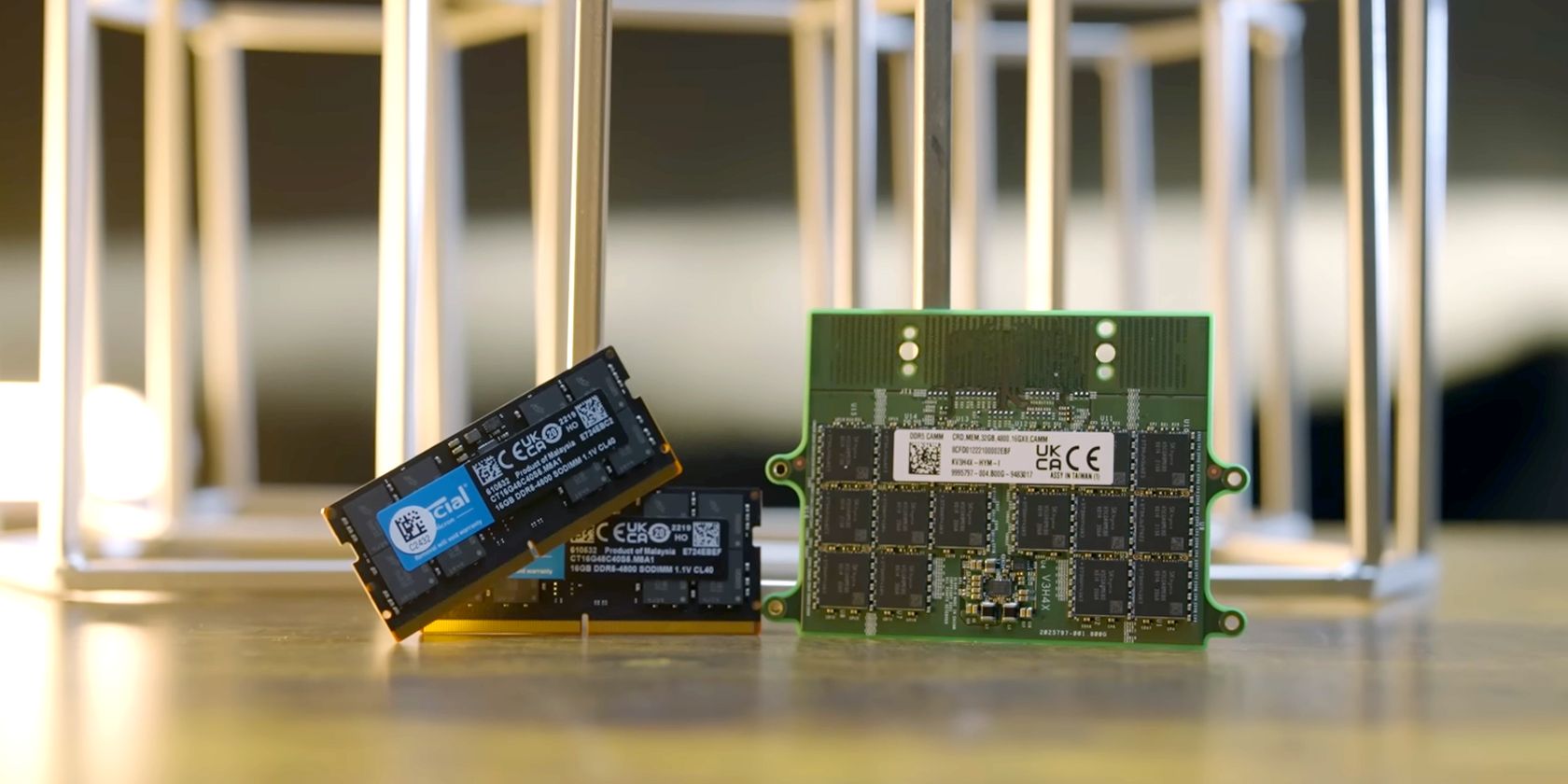
The Genesis of Traditional Memory
For decades, traditional memory modules like DDR (Double Data Rate) SDRAM have been the backbone of computing. Ranging from DDR1 in the early 2000s to today’s high-performing DDR5, traditional memory has powered everything from modest netbooks to sprawling enterprise servers.
Built to be modular, traditional memory relies heavily on DIMMs (Dual Inline Memory Modules) inserted into motherboard slots. This design prioritizes upgradability, letting users swap out sticks for newer, faster alternatives as needed.
However, despite its dominance, traditional memory isn’t without flaws. As devices shrink and demands for compactness and efficiency skyrocket, traditional memory’s bulky architecture is starting to show its limitations.
Camm Memory: The Disruptive Newcomer
Camm Memory, shorthand for Compression Attached Memory Module, is a radical rethinking of how memory can be integrated into computing systems. Unlike conventional DIMMs, Camm Memory mounts flat against the motherboard, slashing the vertical space required.
The compression attachment mechanism offers improved signal integrity and a drastically lower profile, making it an ideal solution for ultra-thin laptops, advanced workstations, and servers where space is at a premium. In essence, Camm Memory isn’t just an upgrade—it’s a paradigm shift.
Key Differences Between Camm Memory vs Traditional Memory
When comparing Camm Memory vs traditional memory, the differences are pronounced across several key dimensions:
1. Physical Design
- Traditional Memory: Utilizes vertical slots with elongated modules protruding from the motherboard.
- Camm Memory: Lies flat against the motherboard, resembling a large chip rather than a stick.
The low-profile nature of Camm Memory is crucial for modern devices, where every millimeter of space matters.
2. Performance and Speed
While both types are capable of blistering speeds, Camm Memory leverages newer technologies that allow for higher data rates with reduced latency. The closer and more stable connection to the motherboard improves efficiency significantly.
3. Scalability
Upgrading traditional memory is straightforward—pop out the old module, pop in the new. With Camm Memory, however, the situation is a bit different. While some implementations allow for replaceable modules, many devices using Camm integrate it in a semi-permanent fashion to preserve form factor and thermal integrity.
4. Durability and Stability
Camm Memory’s compression-based connection reduces the likelihood of loose fittings or poor contact points, which can plague DIMMs over time, especially in mobile devices. In a face-off between Camm Memory vs traditional memory, Camm shows superior resilience in high-mobility environments.
5. Energy Efficiency
Because of the shorter pathways and tighter integration, Camm Memory often requires less power to achieve similar or better performance than traditional setups. This makes it ideal for battery-powered devices and data centers focusing on green energy initiatives.
Advantages of Camm Memory
Enhanced Compactness
Camm Memory’s flat design is a marvel for device manufacturers. Laptops, tablets, and even modular smartphones benefit from the reduced thickness and weight.
Improved Thermal Management
With its closer proximity and compression contacts, Camm Memory enables more efficient heat dissipation. Traditional memory modules can sometimes create localized hot zones, leading to throttled performance or even hardware failure.
Next-Gen Compatibility
As technology moves toward PCIe 5.0 and beyond, traditional designs may struggle with signal integrity. Camm Memory is built with future bandwidth demands in mind, positioning itself as a long-term solution.
Drawbacks of Camm Memory
Upgradability Limitations
One of the longstanding perks of traditional memory has been its plug-and-play flexibility. Camm Memory’s design, while superior in many respects, often complicates easy upgrades, locking users into factory configurations.
Higher Initial Costs
Being a nascent technology, Camm Memory carries a premium. For the average consumer, this could be a deterrent compared to more affordable traditional options.
Repair Complexity
In the event of a failure, replacing Camm Memory might require professional servicing, while replacing a DIMM module can often be a DIY project.
Traditional Memory: Why It’s Still Relevant
Despite the buzz around new innovations, traditional memory isn’t going away overnight. It still holds certain advantages:
- Affordability: Mass production has driven costs down considerably.
- Accessibility: Widely available and supported across countless platforms.
- Flexibility: Easy to upgrade or replace as needed without specialized equipment.
Moreover, for users whose workflows don’t demand bleeding-edge performance—think office tasks, web browsing, or media consumption—traditional memory remains more than sufficient.
Which One Should You Choose?
When considering Camm Memory vs traditional memory, your choice largely hinges on your individual needs:
- Power Users and Gamers: If you require the highest speeds, lowest latency, and best thermal management, Camm Memory is the superior choice—provided you’re ready to pay a premium.
- Everyday Consumers: For general tasks and budget-friendly builds, traditional memory is still incredibly effective.
- Enterprise Solutions: Data centers and cloud providers may increasingly pivot to Camm Memory for its energy efficiency and higher performance capabilities.
Future Trends in Memory Technology
The landscape of memory technology is evolving rapidly. Innovations like HBM (High Bandwidth Memory) and LPDDR (Low Power DDR) for mobile applications are pushing boundaries even further.
However, the competition between Camm Memory vs traditional memory represents a pivotal chapter in this saga. Expect to see hybrid systems emerge, where both types coexist, each playing to its strengths in different parts of the device.
Manufacturers are already exploring modular designs where Camm Memory coexists with replaceable traditional memory, offering a best-of-both-worlds approach.
Final Verdict
The battle between Camm Memory vs traditional memory is emblematic of broader trends in tech: the relentless drive toward efficiency, miniaturization, and performance optimization.
While Camm Memory presents a tantalizing glimpse into the future, traditional memory continues to hold the fort for millions of users worldwide.
Ultimately, the best choice depends on your specific use case, budget, and performance requirements. Those seeking innovation and cutting-edge capability may find Camm Memory to be an irresistible proposition. Meanwhile, traditional memory offers tried-and-true reliability and cost-effectiveness that remains hard to beat.
In a world where technology is constantly evolving, staying informed about developments like these ensures you’re always one step ahead. Whether you’re upgrading your laptop, building a custom gaming rig, or outfitting a server farm, knowing the nuances of Camm Memory vs traditional memory equips you with the knowledge to make the smartest choice possible.
The future is bright, and memory, in all its forms, will continue to fuel the experiences that define our digital lives.










